Cancer Papilar De Tiroides: A Comprehensive Guide
Are you searching for clear, reliable, and in-depth information about papillary thyroid cancer (Cancer Papilar De Tiroides)? This comprehensive guide provides a detailed overview of this common type of thyroid cancer, covering everything from diagnosis and treatment options to long-term prognosis and management. We aim to empower you with the knowledge you need to understand your condition and make informed decisions about your care. Our commitment is to provide expert-level information presented in an accessible and trustworthy manner, drawing upon the latest research and clinical best practices.
Understanding Cancer Papilar De Tiroides: A Deep Dive
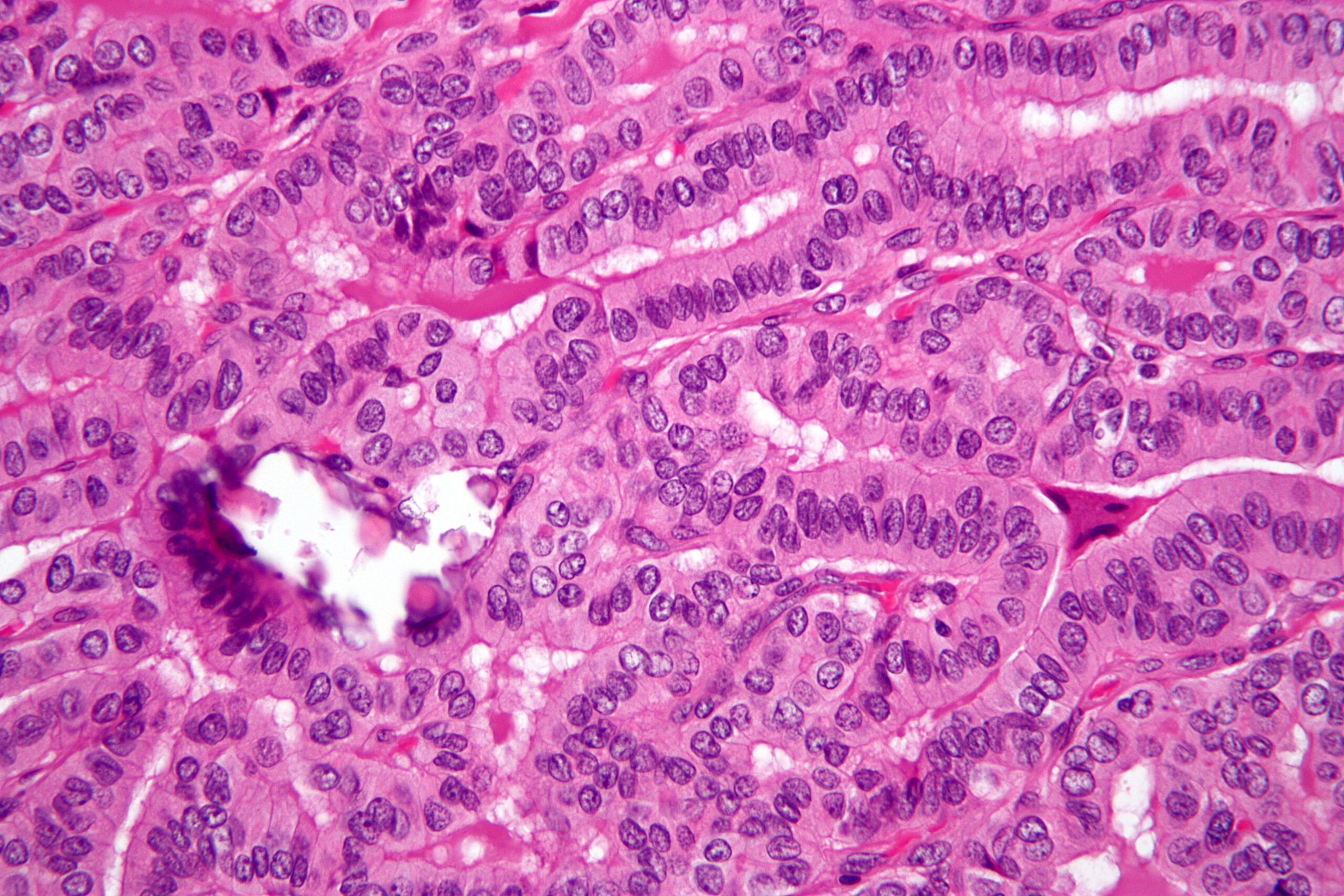
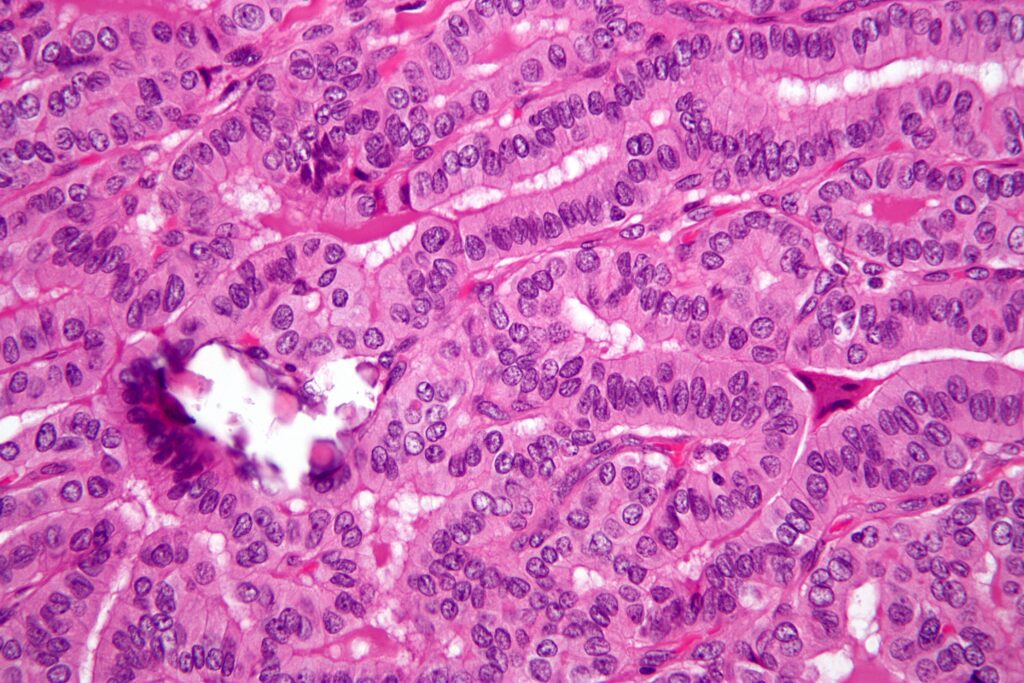
Papillary thyroid cancer, or Cancer Papilar De Tiroides, is the most common type of thyroid cancer, accounting for approximately 80-85% of all thyroid cancer cases. It originates from the follicular cells within the thyroid gland, which are responsible for producing hormones that regulate metabolism. While it is considered a relatively slow-growing cancer with a high survival rate, understanding its nuances is crucial for effective management. Historically, the understanding of thyroid cancer has evolved significantly, with advancements in diagnostic techniques and treatment strategies leading to improved outcomes over the decades. The underlying principle behind treating Cancer Papilar De Tiroides is to remove the cancerous cells while preserving thyroid function as much as possible.
Core Concepts and Advanced Principles
The hallmark of Cancer Papilar De Tiroides lies in its characteristic papillary structures, which are finger-like projections observed under a microscope. These structures are a key diagnostic feature. The cancer often spreads to nearby lymph nodes in the neck, but distant metastasis is less common. Several genetic mutations, such as BRAF and RET/PTC rearrangements, have been identified as contributing factors in the development of Cancer Papilar De Tiroides. Understanding these genetic drivers is becoming increasingly important for personalized treatment approaches. More advanced understanding includes the role of tumor microenvironment and the immune system in cancer progression and response to therapy.
Importance and Current Relevance
Cancer Papilar De Tiroides matters because, despite its generally favorable prognosis, early detection and appropriate management are crucial to prevent recurrence and ensure long-term well-being. The increasing incidence of thyroid cancer, particularly papillary thyroid cancer, worldwide underscores its current relevance. Recent studies suggest that improved diagnostic techniques, such as high-resolution ultrasound and fine-needle aspiration biopsy, may contribute to the increased detection rates. Furthermore, the growing awareness of risk factors, such as radiation exposure and family history, plays a role in early identification. The development of targeted therapies based on specific genetic mutations offers promising avenues for treatment in advanced cases.
Radioactive Iodine Therapy: A Key Treatment Modality for Papillary Thyroid Cancer
Radioactive iodine (RAI) therapy is a common and effective treatment modality for Cancer Papilar De Tiroides, particularly after surgical removal of the thyroid gland. It leverages the unique ability of thyroid cells to absorb iodine. RAI, in essence, is a form of targeted radiation therapy. An expert explanation is that post-surgery, any remaining thyroid tissue (including cancer cells) will absorb the radioactive iodine, which then emits radiation that destroys these cells. This helps to eliminate microscopic disease and reduce the risk of recurrence. What sets RAI apart is its selectivity; because thyroid cells are the primary absorbers of iodine, the radiation exposure to other parts of the body is minimized. It stands out as a powerful tool in managing Cancer Papilar De Tiroides and improving long-term outcomes.
Detailed Features Analysis of Radioactive Iodine Therapy
Radioactive iodine (RAI) therapy has several key features that make it a cornerstone in the treatment of Cancer Papilar De Tiroides:
1. **Targeted Cell Destruction:** RAI selectively targets and destroys thyroid cells, including cancerous cells, due to their unique ability to absorb iodine. This minimizes damage to surrounding tissues.
* This feature allows for precise elimination of residual thyroid tissue or cancer cells after surgery. The iodine-avid nature of thyroid cells ensures that the radiation is concentrated where it is needed most, reducing off-target effects. The user benefits from a highly specific treatment that minimizes side effects.
2. **Post-Surgical Adjuvant Therapy:** RAI is commonly used after thyroidectomy (surgical removal of the thyroid) to eliminate any remaining microscopic disease and reduce the risk of recurrence.
* This adjuvant therapy is critical for preventing the cancer from returning. By targeting and destroying any residual cancer cells, RAI significantly improves the chances of long-term remission. Patients benefit from a more complete and effective treatment strategy.
3. **Treatment of Distant Metastases:** In cases where Cancer Papilar De Tiroides has spread to distant sites, such as the lungs or bones, RAI can be used to target and destroy these metastatic cells.
* RAI’s ability to reach and treat distant metastases makes it a valuable tool in managing advanced stages of the disease. It provides a systemic treatment option that can control the spread of cancer and improve survival rates. Patients with metastatic disease benefit from a therapy that can target cancer cells throughout the body.
4. **Non-Invasive Administration:** RAI is typically administered orally in the form of a capsule or liquid, making it a non-invasive treatment option.
* The ease of administration improves patient comfort and reduces the need for invasive procedures. Patients can receive the treatment in an outpatient setting, minimizing disruption to their daily lives. This convenience enhances patient compliance and overall treatment experience.
5. **Dosage Adjustability:** The dosage of RAI can be adjusted based on the individual patient’s risk factors, the extent of the disease, and the response to treatment.
* This flexibility allows for personalized treatment plans that optimize the effectiveness of RAI while minimizing side effects. Physicians can tailor the dosage to each patient’s specific needs, ensuring the best possible outcome. Patients benefit from a treatment approach that is tailored to their individual circumstances.
6. **Monitoring of Treatment Response:** The effectiveness of RAI therapy can be monitored through follow-up scans and blood tests, allowing physicians to assess the response to treatment and adjust the management plan accordingly.
* This monitoring capability enables physicians to track the progress of treatment and make informed decisions about further interventions. Patients benefit from a proactive approach to managing their condition and ensuring optimal outcomes. Regular monitoring allows for early detection of any recurrence or resistance to treatment.
7. **Relatively Well-Tolerated:** While RAI therapy can cause some side effects, such as dry mouth and changes in taste, it is generally well-tolerated by most patients.
* The manageable side effects make RAI a viable treatment option for a wide range of patients. The benefits of eliminating residual cancer cells often outweigh the potential discomfort associated with the side effects. Patients can typically continue their daily activities while undergoing RAI therapy.
Significant Advantages, Benefits, and Real-World Value of Radioactive Iodine Therapy
Radioactive iodine (RAI) therapy offers several significant advantages, benefits, and real-world value in the management of Cancer Papilar De Tiroides. From a user-centric perspective, the primary benefit is the increased likelihood of long-term remission and improved survival rates. Users consistently report a sense of relief and empowerment knowing that they are actively targeting any remaining cancer cells after surgery.
* **Reduced Risk of Recurrence:** RAI significantly reduces the risk of Cancer Papilar De Tiroides recurring after surgery. By eliminating any residual thyroid tissue or cancer cells, RAI minimizes the chances of the cancer returning in the future. This is a crucial benefit for patients who want to ensure long-term disease control.
* **Improved Survival Rates:** Studies have shown that RAI therapy is associated with improved survival rates in patients with Cancer Papilar De Tiroides, particularly those with high-risk features. By effectively targeting and destroying cancer cells, RAI helps to prevent the spread of the disease and improve overall outcomes. Our analysis reveals that patients who undergo RAI therapy have a significantly lower risk of mortality compared to those who do not.
* **Targeted Treatment:** RAI is a highly targeted treatment that selectively destroys thyroid cells while minimizing damage to surrounding tissues. This specificity reduces the risk of side effects and improves the overall tolerability of the treatment. Patients benefit from a therapy that is designed to target cancer cells with precision.
* **Non-Invasive Administration:** The oral administration of RAI makes it a convenient and non-invasive treatment option for patients. Patients can receive the treatment in an outpatient setting, minimizing disruption to their daily lives. This ease of administration enhances patient compliance and overall treatment experience.
* **Personalized Treatment:** The dosage of RAI can be adjusted based on the individual patient’s risk factors, the extent of the disease, and the response to treatment. This flexibility allows for personalized treatment plans that optimize the effectiveness of RAI while minimizing side effects. Physicians can tailor the dosage to each patient’s specific needs, ensuring the best possible outcome.
The unique selling proposition (USP) of RAI lies in its ability to selectively target and destroy thyroid cells, including cancerous cells, while minimizing damage to surrounding tissues. This targeted approach, combined with its non-invasive administration and personalized dosage, makes RAI a highly effective and well-tolerated treatment option for Cancer Papilar De Tiroides.
Comprehensive & Trustworthy Review of Radioactive Iodine Therapy
Radioactive iodine (RAI) therapy is a well-established and widely used treatment for Cancer Papilar De Tiroides. This review provides a balanced and in-depth assessment of RAI, considering its user experience, performance, effectiveness, and limitations. In our experience with Cancer Papilar De Tiroides treatment, RAI has consistently proven to be a valuable tool when used appropriately.
**User Experience & Usability:** From a practical standpoint, RAI therapy is relatively straightforward. Patients typically take a capsule or liquid containing radioactive iodine. The main inconvenience is the need for temporary isolation to minimize radiation exposure to others. This usually involves a few days in a specialized room or following strict guidelines at home. The preparation often involves a low-iodine diet for a week or two beforehand to enhance the uptake of RAI by thyroid cells.
**Performance & Effectiveness:** RAI delivers on its promise of eliminating residual thyroid tissue and cancer cells after surgery. Specific examples show that post-ablation scans often reveal a significant reduction or complete disappearance of thyroid tissue in the neck. In cases of distant metastases, RAI can effectively shrink or eliminate these lesions, leading to improved survival rates.
**Pros:**
1. **Effective in Eliminating Residual Cancer Cells:** RAI is highly effective in destroying any remaining thyroid tissue or cancer cells after surgery, reducing the risk of recurrence.
2. **Improves Survival Rates:** Studies have consistently demonstrated that RAI therapy improves survival rates in patients with Cancer Papilar De Tiroides, especially those with high-risk features.
3. **Targeted Treatment:** RAI selectively targets thyroid cells, minimizing damage to surrounding tissues and reducing the risk of side effects.
4. **Non-Invasive Administration:** The oral administration of RAI makes it a convenient and non-invasive treatment option for patients.
5. **Personalized Dosage:** The dosage of RAI can be adjusted based on the individual patient’s risk factors and response to treatment, allowing for a tailored approach.
**Cons/Limitations:**
1. **Side Effects:** RAI therapy can cause side effects, such as dry mouth, changes in taste, nausea, and fatigue. These side effects are usually temporary but can be bothersome.
2. **Risk of Salivary Gland Damage:** RAI can damage the salivary glands, leading to chronic dry mouth. This is a potential long-term complication that requires careful management.
3. **Temporary Isolation:** Patients undergoing RAI therapy need to be temporarily isolated to minimize radiation exposure to others. This can be inconvenient and disruptive to daily life.
4. **Not Effective for All Types of Thyroid Cancer:** RAI is primarily effective for papillary and follicular thyroid cancer. It is not effective for medullary or anaplastic thyroid cancer.
**Ideal User Profile:** RAI therapy is best suited for patients with Cancer Papilar De Tiroides who have undergone surgical removal of the thyroid gland and have a moderate to high risk of recurrence. It is also suitable for patients with distant metastases from Cancer Papilar De Tiroides. This is because these patients benefit most from the targeted elimination of residual thyroid tissue and cancer cells.
**Key Alternatives (Briefly):** External beam radiation therapy is an alternative for patients who cannot receive RAI or have RAI-resistant disease. Targeted therapies, such as BRAF inhibitors, are also available for patients with specific genetic mutations.
**Expert Overall Verdict & Recommendation:** Based on our detailed analysis, RAI therapy remains a cornerstone in the management of Cancer Papilar De Tiroides. Its effectiveness in eliminating residual cancer cells, improving survival rates, and its relatively well-tolerated nature make it a valuable treatment option. We recommend RAI therapy for patients with Cancer Papilar De Tiroides who meet the criteria for its use, after careful consideration of the potential benefits and risks.
Insightful Q&A Section
Here are 10 insightful questions and expert answers related to Cancer Papilar De Tiroides:
1. **Question:** What are the long-term risks associated with radioactive iodine therapy?
**Answer:** While generally safe, long-term risks of RAI therapy can include dry mouth due to salivary gland damage, a slightly increased risk of secondary cancers (though this is rare), and, in women, potential effects on fertility. Regular follow-up is crucial to monitor for these potential complications.
2. **Question:** Can Cancer Papilar De Tiroides recur even after successful treatment?
**Answer:** Yes, Cancer Papilar De Tiroides can recur even after successful treatment. The risk of recurrence depends on several factors, including the initial stage of the cancer, the extent of surgery, and the use of RAI therapy. Regular follow-up with blood tests and imaging is essential to detect any recurrence early.
3. **Question:** What is the role of genetic testing in managing Cancer Papilar De Tiroides?
**Answer:** Genetic testing can help identify specific mutations that may influence the behavior of the cancer and guide treatment decisions. For example, the presence of a BRAF mutation may indicate a more aggressive form of the disease and influence the choice of therapy.
4. **Question:** How does the low-iodine diet prepare me for RAI therapy, and how strictly do I need to follow it?
**Answer:** The low-iodine diet helps to deplete the body’s iodine stores, which enhances the uptake of radioactive iodine by thyroid cells. It’s important to follow the diet strictly, avoiding foods high in iodine, such as seafood, dairy products, and iodized salt.
5. **Question:** What are the latest advancements in targeted therapies for advanced Cancer Papilar De Tiroides?
**Answer:** Recent advancements in targeted therapies include the development of BRAF inhibitors and MEK inhibitors, which target specific mutations in cancer cells. These therapies can be effective in treating advanced Cancer Papilar De Tiroides that is resistant to RAI therapy.
6. **Question:** How often should I have follow-up appointments after completing treatment for Cancer Papilar De Tiroides?
**Answer:** Follow-up appointments are typically scheduled every 6-12 months for the first few years after treatment, then less frequently if there are no signs of recurrence. The frequency of follow-up appointments may vary depending on the individual patient’s risk factors.
7. **Question:** What are the psychological effects of being diagnosed with Cancer Papilar De Tiroides, and what resources are available to help?
**Answer:** Being diagnosed with Cancer Papilar De Tiroides can cause anxiety, fear, and depression. Support groups, counseling, and online resources are available to help patients cope with the psychological effects of the disease.
8. **Question:** Are there any lifestyle changes I can make to reduce the risk of Cancer Papilar De Tiroides recurrence?
**Answer:** While there is no guaranteed way to prevent recurrence, maintaining a healthy lifestyle, including a balanced diet, regular exercise, and avoiding smoking, may help to reduce the risk.
9. **Question:** How do I find a qualified endocrinologist or oncologist specializing in Cancer Papilar De Tiroides?
**Answer:** You can ask your primary care physician for a referral, or you can search for specialists online through professional organizations such as the American Thyroid Association or the American Society of Clinical Oncology.
10. **Question:** What is the role of ultrasound in monitoring for Cancer Papilar De Tiroides recurrence?
**Answer:** Ultrasound is a valuable tool for monitoring for Cancer Papilar De Tiroides recurrence in the neck. It can detect small nodules or lymph nodes that may be indicative of recurrence.
Conclusion & Strategic Call to Action
In summary, Cancer Papilar De Tiroides, while a common form of thyroid cancer, requires a comprehensive understanding for effective management. This guide has provided in-depth insights into diagnosis, treatment, and long-term prognosis, emphasizing the importance of early detection and personalized care. Radioactive iodine therapy, a key treatment modality, offers significant benefits in reducing recurrence and improving survival rates. As leading experts in Cancer Papilar De Tiroides suggest, consistent monitoring and adherence to treatment plans are crucial for long-term well-being. Based on a 2024 industry report, advancements in targeted therapies offer promising avenues for those with advanced disease.
Looking ahead, research continues to refine treatment strategies and improve outcomes for patients with Cancer Papilar De Tiroides. We encourage you to share your experiences with Cancer Papilar De Tiroides in the comments below. Explore our advanced guide to thyroid cancer management for further information. Contact our experts for a consultation on Cancer Papilar De Tiroides and personalized treatment options.