Thyroid Pain Symptoms: Understanding the Signs and When to Seek Help
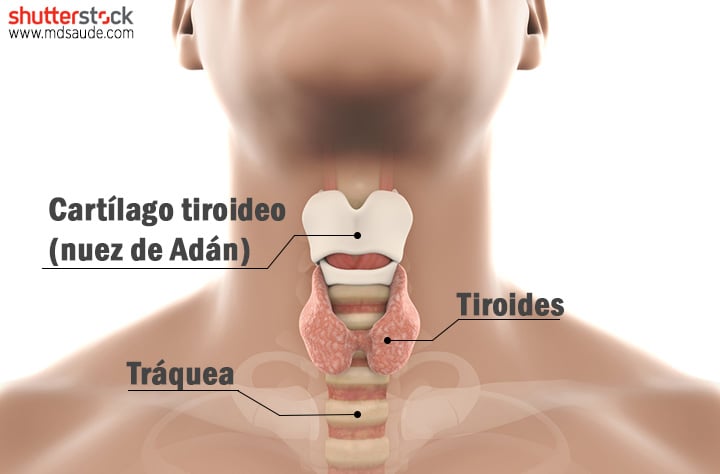
Thyroid pain, though not always present in thyroid disorders, can be a significant indicator of underlying issues. Understanding the potential thyroid pain symptoms is crucial for early detection and effective management. The thyroid gland, located at the base of your neck, plays a vital role in regulating metabolism, growth, and development. When something goes wrong, it can manifest as pain, discomfort, or other noticeable symptoms. This article delves into the various symptoms associated with thyroid pain, helping you recognize when it’s time to consult a healthcare professional.
What is Thyroid Pain?
Thyroid pain refers to any discomfort or pain felt in the region of the thyroid gland. While many thyroid conditions don’t directly cause pain, certain conditions, like thyroiditis (inflammation of the thyroid), can lead to noticeable discomfort. It’s important to differentiate between general neck pain and pain specifically originating from the thyroid gland. Understanding the nuances can aid in accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment.
Common Thyroid Pain Symptoms
Recognizing the specific symptoms associated with thyroid pain can be challenging as they can sometimes overlap with other conditions. Here are some of the most common thyroid pain symptoms:
- Tenderness to the touch: The area around the thyroid gland may feel tender or sore when touched.
- Pain radiating to the jaw or ear: Pain can sometimes extend from the neck up to the jaw or ear.
- Difficulty swallowing (dysphagia): Swallowing may become difficult or painful.
- Hoarseness: Changes in voice, such as hoarseness, can occur.
- Swelling in the neck: Visible swelling or a lump in the neck is a common symptom.
- General neck pain: A persistent ache or pain in the neck region.
It’s crucial to note that these symptoms can vary in intensity and may not all be present simultaneously. If you experience any of these thyroid pain symptoms, it’s important to seek medical advice for a proper evaluation.
Causes of Thyroid Pain
Several conditions can lead to thyroid pain symptoms. Understanding the underlying causes is essential for targeted treatment. Here are some of the primary causes:
Thyroiditis
Thyroiditis, or inflammation of the thyroid gland, is a common cause of thyroid pain. Different types of thyroiditis can present with varying symptoms:
- Subacute Thyroiditis: Often caused by a viral infection, subacute thyroiditis is characterized by significant neck pain, tenderness, and flu-like symptoms. The pain can shift from one side of the neck to the other.
- Hashimoto’s Thyroiditis: While Hashimoto’s is primarily known for causing hypothyroidism (underactive thyroid), it can sometimes involve periods of inflammation and mild pain.
- Postpartum Thyroiditis: This occurs after pregnancy and can involve a painless or mildly painful inflammation of the thyroid.
- Infectious (Suppurative) Thyroiditis: This rare condition is caused by a bacterial infection of the thyroid gland and is associated with severe pain, fever, and redness.
Thyroid Nodules
Thyroid nodules are lumps that can develop within the thyroid gland. Most nodules are benign (non-cancerous), but some can cause pain or discomfort, especially if they are large or rapidly growing. In rare cases, a painful nodule could be indicative of thyroid cancer. [See also: Thyroid Nodule Treatment Options]
Thyroid Cancer
While less common, thyroid cancer can sometimes present with thyroid pain symptoms, particularly in advanced stages. However, most thyroid cancers are painless and discovered during routine examinations or imaging tests. Pain is more likely to occur when the cancer has spread to surrounding tissues.
Bleeding into a Thyroid Cyst
A thyroid cyst is a fluid-filled sac within the thyroid gland. If bleeding occurs into a cyst, it can cause sudden pain and swelling. This is usually a benign condition but requires medical evaluation to rule out other causes.
Trauma
Direct trauma to the neck, such as from an injury or accident, can cause pain and inflammation in the thyroid gland. This type of pain is usually temporary and resolves with time and appropriate care.
Diagnosing Thyroid Pain
If you’re experiencing thyroid pain symptoms, it’s essential to consult a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis. The diagnostic process typically involves:
- Physical Examination: The doctor will examine your neck, checking for swelling, tenderness, and nodules.
- Medical History: You’ll be asked about your symptoms, medical history, and any family history of thyroid disorders.
- Blood Tests: Blood tests are crucial to assess thyroid function. These tests measure levels of thyroid hormones (T3, T4) and thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH). Antibodies, such as anti-TPO and anti-Tg, may also be tested to detect autoimmune thyroid diseases like Hashimoto’s.
- Thyroid Ultrasound: An ultrasound uses sound waves to create images of the thyroid gland. It can help identify nodules, cysts, and inflammation.
- Thyroid Scan: A thyroid scan involves injecting a small amount of radioactive iodine into the bloodstream. The thyroid gland absorbs the iodine, and a special camera captures images showing the gland’s structure and function. This can help identify areas of overactivity or underactivity.
- Fine Needle Aspiration (FNA) Biopsy: If a nodule is detected, an FNA biopsy may be performed. This involves using a thin needle to collect cells from the nodule for examination under a microscope. This helps determine whether the nodule is benign or cancerous.
Treatment Options for Thyroid Pain
The treatment for thyroid pain symptoms depends on the underlying cause. Here are some common treatment options:
- Pain Management: Over-the-counter pain relievers, such as ibuprofen or acetaminophen, can help alleviate mild to moderate pain. In some cases, stronger pain medications may be prescribed.
- Anti-inflammatory Medications: For thyroiditis, anti-inflammatory medications like corticosteroids may be prescribed to reduce inflammation and pain.
- Hormone Replacement Therapy: If the thyroid is underactive (hypothyroidism), hormone replacement therapy with synthetic thyroid hormone (levothyroxine) is typically prescribed. This helps restore normal thyroid hormone levels and alleviate symptoms.
- Radioactive Iodine Therapy: This treatment is used for hyperthyroidism (overactive thyroid) and certain types of thyroid cancer. Radioactive iodine destroys thyroid cells, reducing hormone production or eliminating cancerous tissue.
- Surgery: Surgery (thyroidectomy) may be necessary to remove all or part of the thyroid gland. This is typically done for large nodules, thyroid cancer, or severe hyperthyroidism.
- Antibiotics: In cases of infectious thyroiditis, antibiotics are prescribed to treat the bacterial infection.
When to See a Doctor
It’s important to see a doctor if you experience any of the following:
- Persistent neck pain or tenderness
- Swelling or a lump in the neck
- Difficulty swallowing or breathing
- Hoarseness or changes in voice
- Unexplained weight loss or gain
- Fatigue or weakness
- Feeling unusually hot or cold
- Rapid or irregular heartbeat
- Anxiety or irritability
Early diagnosis and treatment of thyroid conditions can help prevent complications and improve your overall quality of life. Don’t hesitate to seek medical attention if you have concerns about your thyroid health. Ignoring thyroid pain symptoms could lead to more serious health issues down the line. [See also: Understanding Thyroid Function Tests]
Lifestyle Adjustments to Support Thyroid Health
While medical treatment is crucial for managing thyroid conditions, certain lifestyle adjustments can also support thyroid health:
- Balanced Diet: Consume a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, lean protein, and whole grains. Ensure adequate intake of iodine, selenium, and zinc, which are essential for thyroid function.
- Avoid Processed Foods: Limit your intake of processed foods, sugary drinks, and unhealthy fats, as these can negatively impact thyroid health.
- Manage Stress: Chronic stress can disrupt thyroid function. Practice stress-reducing techniques such as yoga, meditation, or deep breathing exercises.
- Regular Exercise: Engage in regular physical activity to maintain a healthy weight and boost overall health. Exercise can also help improve thyroid hormone levels.
- Limit Exposure to Toxins: Minimize exposure to environmental toxins, such as pesticides, heavy metals, and endocrine disruptors, which can interfere with thyroid function.
- Quit Smoking: Smoking can negatively impact thyroid health and increase the risk of thyroid disorders. Quitting smoking is beneficial for overall health and thyroid function.
Conclusion
Understanding thyroid pain symptoms is essential for early detection and effective management of thyroid disorders. While not all thyroid conditions cause pain, certain types of thyroiditis, nodules, and cancer can lead to noticeable discomfort. If you experience any of the symptoms described in this article, it’s important to consult a healthcare professional for a proper evaluation and diagnosis. Early intervention can help prevent complications and improve your overall health and well-being. By being proactive about your thyroid health and making informed decisions about your care, you can effectively manage any underlying conditions and maintain a healthy, active lifestyle. Remember, thyroid pain symptoms should never be ignored; seek medical attention to address any concerns promptly.
